How To Build Hydro Electric Power Plant
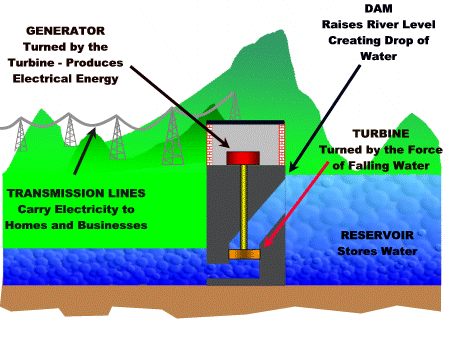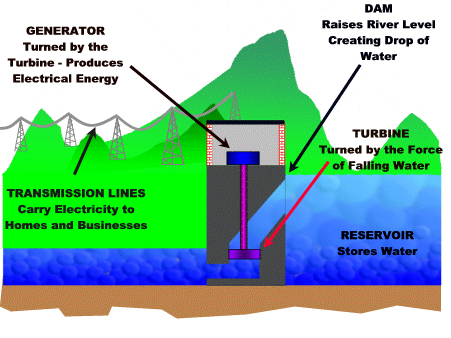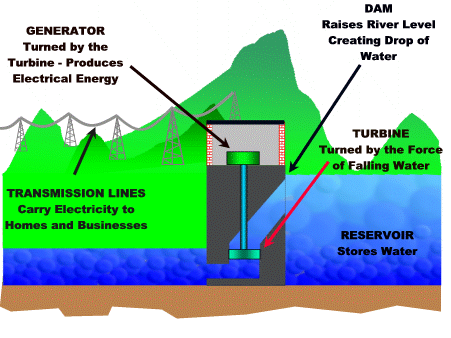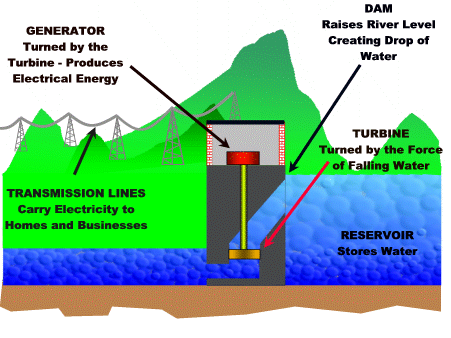
How To Build Hydro Electric Power Plant & How Hydropower Plants Work Hydropower plants capture the energy of falling water to generate electricity. A turbine converts the kinetic energy of falling water into mechanical energy. Then a generator converts the mechanical energy from the turbine into electrical energy. Hydroplants range in size from "micro-hydros" that power only a few homes to giant dams like Hoover Dam that provide electricity for millions of people. The photo on the right shows the Alexander Hydroelectric Plant on the Wisconsin River, a medium-sized plant that produces enough electricity to serve about 8,000 people. Parts of a Hydroelectric Plant Most conventional hydroelectric plants include four major components (see graphic below): Dam. Raises the water level of the river to create falling water. Also controls the flow of water. The reservoir that is formed is, in effect, stored energy. Turbine. The force of falling water pushing against...